The Problems of Earth: Demand for raw materials
The demand for raw materials is the need of basic materials or substances that are used to produce goods.
Example of metallic raw materials (KWG industries, 2021)
Over the coming years, the situation on the raw materials markets is likely to remain tense as large countries such as China, India and Brazil press ahead with infrastructural development and industrialization. As part of this trend, the industrialized countries are losing influence, and weaker developing countries are becoming even more marginalized.
City of Ahmedabad, the 5th largest city in India and the 3rd fastest growing city in the world (scoopwhoop, 2014)
Resource conflicts are erupting and highly developed countries are determined to safeguard their access to raw materials. As an example, the European Union is almost entirely reliant on imports. The situation is specially critical in relation to certain strategic metals which will continue to be essential for key growth technologies in the foreseeable future. Nickel, tin, coper and lead are some examples of raw materials which prices have been rising since 2,000.
Rising prices can be observed for some strategic commodities used in growth industries, for which there is no prospect of a short-term substitute. There is some concern that no substitute is likely to be identified for various metals used in the industrialization process or for high-tech needs: bottlenecks are predicted for the platinum need for the production of fuel cells for solar panels and the high price of steel is likely to remain an obstacle to the expansion of wind power.
Construction of an offshore wind farm facility (Windpower, 2017)
The increasing demand of raw materials has a socio-economic impact, the fact that we will run out of them since the earth is finite, and an environmental impact. Mining and oil exploration and extraction damage vast extensions of land and sea and pollutes ecosystems. The leftovers, obsolete and broken products that result from this raw materials have a surprising environmental cost. Almost 3 million kilos of discarded electronics are already processed monthly at a single giant recycling plant in California. Global electronic waste (e-waste) generation is growing by about 40 million tonnes yearly, but only the 10% of the e-waste is recycled. Millions of tones of it are dumped in countries such as Kenya.
Child in an e-waste landfill in Kenya (PC magazine, 2011).
Raw materials are mainly minerals that are obtained by means of primary production. But their extraction has issues such as the environmental impacts and their socio-economic role in development processes. A few countries in Latin America and Africa possess some of the world’s largest reserves of mineral resources and are emerging as major suppliers. The term “resources” is used to denote stocks of raw materials, the lower the availability of these stocks, the more urgent the problem of raw materials appears to be. It is essential to bear in mind that the concentration of raw material deposits and their extractability can vary over time.
The current demand for raw materials comes mainly from populous countries with high level of purchasing power which are investing in industries and infrastructure. Unfortunately, there is no empirical evidence to support the hypothesis that improved economic performance is accompanied by a reduction in raw materials consumption.
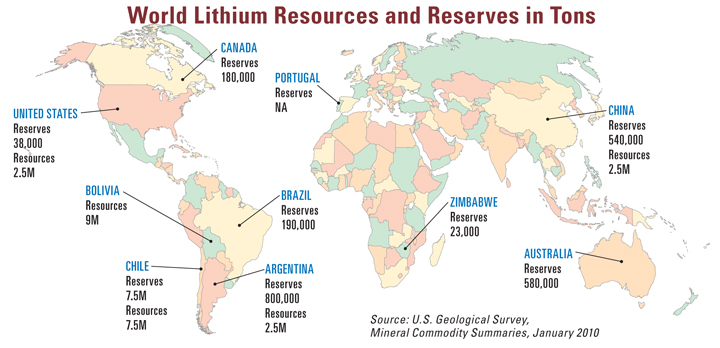
World’s lithium deposits (Site Selection Magazine, 2011)
Political and institutional deficits determine the economic success of failure. Countries that have neglected to develop associated sectors such as refineries for the extracted raw materials –making them dependent on imported goods– or agriculture –causing hunger an poverty. These situations frequently involve a high level of corruption.
In our society, we always have to have the new, best product. In 2017, Americans spent on communication equipment 5 times what they spent in 2010. With this systematic “get rid of what’s old”, e-waste is the world’s fastest-growing solid-waste stream. It is on us to change it, but that stream is expected to turn into a torrent as the world upgrades to 5G. That’s bad news, as e-waste can contain harmful materials that pose environmental risks.
The growing demand of raw materials has been a crucial factor for the price increases since 2,000, specially China, fed by the occidental demand for goods. China is now the World’s largest importer of raw materials and the second largest importer of crude oil after the USA.
Worker in construction site in Beijing (World Finance, 2014)
Key factors are the demand for capital goods of consumer demand, the urbanization trend and industrialization. Raw materials are tightly linked with energy shortages, food supply, environmental and health problems and social conflicts and injustice. Nonetheless, other emerging economies such as India and Brazil is also important. Forecasts show that these countries have good prospects of development with above average rates of growth.
Resource extraction is linked to major intervention in the ecosystem, producing toxic substances and using large quantities of water and energy. Moreover, the transport of raw materials from remote areas also requires its infrastructure. Raw materials exploration and extraction are being carried out in areas which are highly sensitive in geo-ecological terms –such as nature protected areas, deep sea or continental shelves. Later stages in the raw materials lifecycle cause further environmental damage. On a socio-economic scale, it is important to remark that the exploration, extraction and the late dumping grounds of the remains of those raw materials or their consequent goods happen on politically unstable regions.
Mining exploration acrtivity (Fugro, 2021)
What can we do?
To resolve these conflicts new forms of governance are needed, based on international cooperation, greater resource productivity and sustainable resource management in a process which must involve companies and NGOs alike. The options can be summed up as a “3-M strategy”: Material productivity, Market transparency and Multilateral cooperation. The European Commission proposed the establishment of an international panel on the sustainable use of natural resources in 2005, and despite there has been an improvement, it hasn’t been enough.
Countries that invest their raw materials export revenue in a designated fund which they use to purchase securities and are free from debt, can invest in other sectors and have stable social and legal systems. A proper management of a country’s resources is essential to have a healthy environment and socio-economic system.
Applying rules for specific trash and investing in making things easier to recycle materials, specially those which are potentially polluters is critical. An other solution is to make things last as long as they once did. Yer instead, technology companies are speeding the pace of obsolescence.
eZcycle e-waste rcycling spot (Marketing strategies & solutions, 2021)
Some companies are increasing their recycling efforts on their own. Whether if it is for the economic benefit or the public relations boos, it means that there is a concern about what the public –and customers– think. An enterprise seen as “green” or environmental concerned will increase sells.
As consumers, it is important to keep in mind that even if the extraction technologies and logistics have cut supplier costs in the past and it resulted in price cuts, it does not mean that the supply is better or there is plenty of raw materials to continue its consumerism. It is important to reuse and recycle our goods as they can be disassembled and give life to new ones. Sometimes there are products that cannot be disassembled because of how they are made, but it is our duty as customers to push enterprises for making products that can be easily recycled, so their pieces can be reused and their materials can be transformed into raw materials again.
E-waste Recycling Virginia Company (Article Techs, 2019)
“Nature is our biggest ally and our greatest inspiration” – David Attenborough
Maria Serra
SOURCES
Banton, C. (2020) Raw Materials. Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/r/rawmaterials.asp
Bleischwitz, R. (2007) International Raw Materials Markets: Rising Prices and Growing Conflict Potential. Global Trends 2007.
Carrara, S. et al. (2020) Raw materials demand for wind and solar PV technologies in the transition towards a decarbonized energy system. Publications Office of the European Union. DOI:10.2760/160859 https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/publication/raw-materials-demand-wind-and-solar-pv-technologies-transition-towards-decarbonised-energy-system
PC Tech (2011) E-waste and the need for secure disposal mechanisms. PC magazine. https://pctechmag.com/2011/09/e-waste-and-the-need-for-secure-disposal-mechanisms/
Pilcher, G.R. (2018) The Demand for Coatings Raw Materials to 2022. European Coatings Journal, CoatingsTech(14,5). https://www.paint.org/coatingstech-magazine/articles/demand-coatings-raw-materials-to-2022/
Semuels, A. Calif, F. (2019) The World Has an E-Waste Problem. Time. https://time.com/5594380/world-electronic-waste-problem/












Comments
Post a Comment